When will the new crown lift the global state of emergency?
According to Xinhua news agency, on January 30, local time, WHO announced on its official website that although the new pandemic may be approaching a turning point, it still constitutes a “public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC)”. This is the highest level of alert issued by the WHO.
In response, Professor Zeng Guang, former chief epidemiologist at the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, was interviewed, according to the Health Times client.

File photo
Why continue to maintain the new crown global emergency?
Zeng Guang said, “According to the World Health Organization, the global average daily death toll in the recent week is nearly 10,000. Standing in the perspective of global epidemic prevention, this statement is more of a more cautious attitude, but also in line with the reality of China, is desirable and acceptable.”
What is the current status of the spread of the epidemic in China as well as its prevention and control?
Zeng Guang said, “Combined with China’s own reality, 80% to 90% of the population has now acquired natural immunity after natural infection, plus the domestic vaccination rate has reached a level of more than 90%, China’s immune barrier has been basically established. Although in the short term, the epidemic situation is safe and the storm has passed, in the medium to long term, there are still many variables.”
Zeng Guang further explained that, on the one hand, China still faces the risk of overseas importation of XBB, BQ.1 and their subbranches, and the elderly who have not yet been vaccinated also remain at risk of infection; on the other hand, after the full liberalization of this new crown outbreak, both the medical treatment system and the public health system need to sum up their experiences. Therefore, China will have to make a final decision taking into account not only the state of the disease epidemic, morbidity and mortality, but also the needs of economic development, social stability, and international exchange.
What are the conditions under which the future globally recognized new crown no longer constitutes a state of emergency?
Zeng Guang pointed out, “The primary criterion for judgment is the mortality rate. Because neo-crown infections are persistent, the global epidemic situation will only continue to improve if no new mutant strains with high mortality rates emerge. The WHO committee’s call for long-term public health action is designed to prioritize the reduction of neo-crown morbidity and mortality and does not close the doors that individual countries have just opened again; the global epidemic prevention has now taken a major step forward, and the overall epidemic situation still continues to move in a moderate direction.”
“It should be reminded that due to the long-term existence of the new crown virus, even if the WHO will one day lift the emergency status of the new crown epidemic in the future, it needs to issue a reminder at the same time, at least as it did with influenza, to treat the new crown as a key infectious disease for global surveillance and to guide countries to establish routine surveillance systems.” Zeng Guang stressed.
World Health Organization: the new crown outbreak still constitutes a “public health emergency of international concern”

Tadese
The WHO Emergency Committee held its 14th meeting on Jan. 27, local time, to discuss whether the New Guinea outbreak continues to constitute a “public health emergency of international concern,” according to the New Beijing News. After the meeting, WHO Director-General Tandezai followed the committee’s recommendation and confirmed that the new crown outbreak still constitutes a “public health emergency of international concern.
In a statement, WHO said Director-General Tandezai endorsed the Emergency Committee’s view that the New Crown pandemic is at a turning point. He expressed appreciation for the committee’s recommendations in making a prudent transition to mitigate potential negative impacts.
“As we enter the fourth year of the pandemic, we are certainly in a much better position now than we were a year ago.” At the peak of the Omicron epidemic, more than 70,000 deaths were reported to the WHO each week, Tandse said. By October of last year, however, that number had dropped to less than 10,000, near the lowest level since the new crown pandemic.
To date, there have been more than 670 million cases of new crown infections and more than 6.7 million deaths worldwide.
The new crown virus can not be transmitted? CDC: China’s current round of the epidemic is nearing the end
“During the Spring Festival holiday, the epidemic did not rebound significantly, and no new mutant strains were found throughout the epidemic, and the current round of the epidemic in China is nearing its end.” This is how the latest issue of China CDC Weekly (China Center for Disease Control Weekly) summarizes the “Overview of National Novel Coronavirus Infection Diagnosis and Surveillance Data” (hereinafter referred to as “Overview”).
According to Red Star News, a recent national outbreak of novel coronavirus infections released by the CDC showed a downward trend in the rate of new coronavirus infections. Experts believe that the situation is not a change in the virus itself, but is related to the formation of an immune barrier from previous large-scale population infections, which will slow down the spread of the virus in the short term. There is still a possibility of a peak in the later period, but the situation will not be as severe as it was at the end of last year.
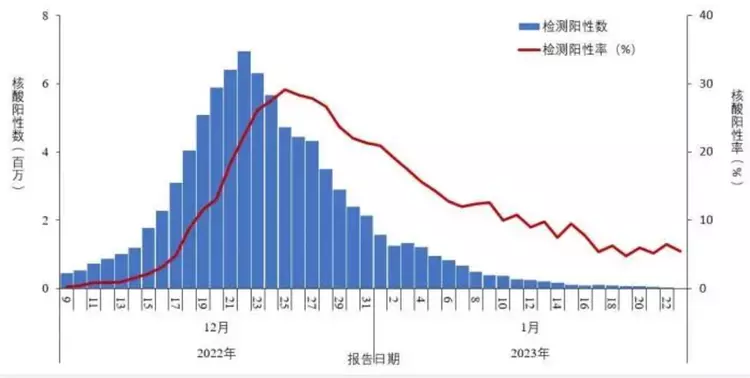
Trends in the number of positive nucleic acid tests and positive rates for novel coronaviruses in reported populations nationwide Image source: Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention
According to the national outbreak of novel coronavirus infection released on the official website of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) on December 25, the number of positive nucleic acid tests and the rate of positive tests in the population reported by provinces from December 9, 2022 to January 23, 2023 showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. upload antigen test results. The results showed that provinces reported lower antigen testing, showing a gradual decrease trend.
According to Health Times 27, for the decreasing trend shown by the infection rate of the new coronavirus, Professor Fang Bangjiang, director of the Institute of Acute and Critical Care of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, explained that “the gradual weakening of the spread of the new coronavirus is not due to important changes in the virus itself, but the social side maintains a certain low level of transmission and consolidates the immune barrier, plus the vast majority of people are infected, forming a herd immunity, the virus is somewhat ‘not spreading’ anymore.”

Average Rating